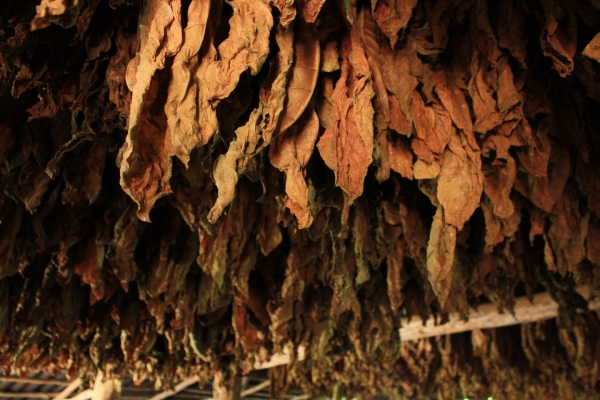
Virginia tobacco leaf drying process is one of the most important parts of tobacco leaf processing. If you plan to grow your own Virginia tobacco, knowing how to properly care for and dry the leaves is essential to achieving the best quality.
Virginia tobacco drying is a critical step in tobacco production that has a direct impact on the quality and final price of the product.
The stages of drying Virginia tobacco leaves. The stages of drying Virginia tobacco leaves
Harvesting tobacco: Virginia tobacco leaves are first harvested from the orchards.

Distillation: The harvested leaves are distilled to evaporate their excess water.

Drying: Distilled leaves are hung in the shade to dry slowly. This step may take several weeks.

Humidification: After drying, the leaves are returned to the optimal humidity for tobacco production using humidification devices.
Packaging: Tobacco leaves are packed and ready for use in the cigarette industry.

The importance of drying tobacco leaves
Quality maintenance: This process is necessary to maintain the quality of Virginia and Basma tobacco. Tobacco that is not dried well leads to a decrease in the quality of the cigarette.
Preserving color and flavor: Proper drying helps preserve the natural color and flavor of tobacco, which is important for producing quality cigarettes.
Increased shelf life: Cured tobacco is more durable and can be used for a longer period of time. Wet tobacco spoils faster and is not suitable for packaging and transportation.
Improved storability: Cured tobacco has better storability and can be stored for a longer period of time without loss of quality.
Virginia tobacco drying and storage process: from harvest to storage
Harvesting Virginia tobacco leaves
Harvest time: The best time to harvest Virginia tobacco leaves and burley tobacco leaves is when the leaves have turned bright yellow or golden. This usually happens 6 to 8 weeks after planting.
Harvesting method: To harvest the leaves, gently separate them from the stem. Be careful not to damage the leaves.
Selection of leaves: Only harvest healthy, unblemished leaves. Damaged or spotted leaves should be discarded.

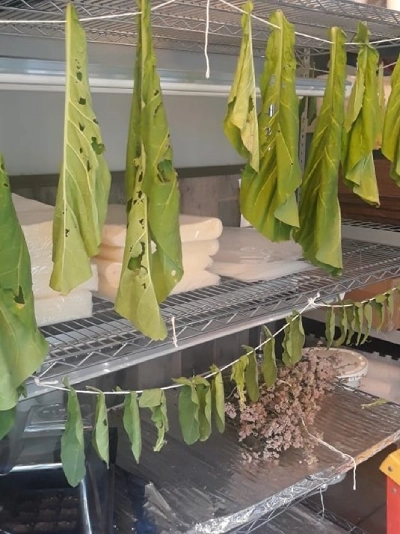
Virginia tobacco leaf wilt
Purpose: The wilting of the leaves removes their excess moisture and makes the drying process easier.
Method: Hang the harvested leaves in a warm and shady place. The ideal temperature for wilting is between 20 and 25 degrees Celsius.
Duration: The duration of wilting depends on the thickness of the leaves and environmental conditions. In general, it takes 2 to 4 days for the leaves to wilt completely.

Drying Virginia tobacco leaves
Different methods: There are several different methods for drying Virginia tobacco leaves, including:
- Air drying: This is the easiest method, but it requires suitable weather conditions. Hang the leaves in a warm, dry, well-ventilated place.
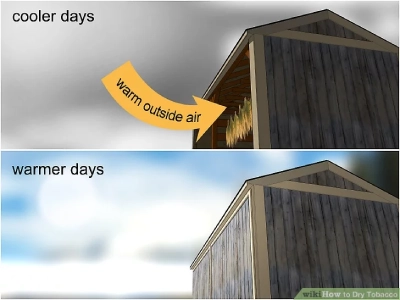
- Storage drying: This method allows more control over the drying process. Hang the leaves in a well-ventilated warehouse or room and adjust the temperature and humidity.
- Smoke drying: This traditional method gives the leaves a smoky flavor and aroma. Hang the leaves in a room with cool, dry smoke.
- Duration: The drying time of the leaves depends on the thickness of the leaves, drying method and environmental conditions. Generally, it takes 2 to 4 weeks for the leaves to dry completely.
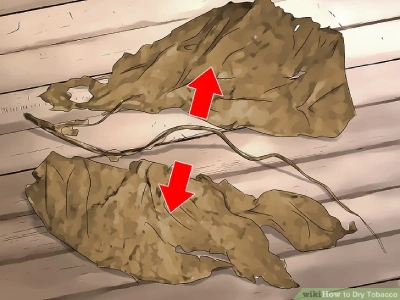
Symptoms of complete drying of Virginia tobacco leaves
- The leaves become brittle and dry.
- The color of the leaves changes from light yellow to dark brown.
- The stem of the leaves is easily crushed.
- The leaves have a strong tobacco smell.
Storage of dried Virginia tobacco leaves
- Dried Virginia tobacco leaves should be stored in a cool, dry and dark place.
- Store leaves in closed containers such as wooden boxes or jars.
- The relative humidity of the air should be between 60 and 70%.
- The air temperature should be between 10 and 20 degrees Celsius.
Therefore, the Virginia tobacco drying process plays a key role in tobacco production and has a significant impact on maintaining the quality, color, flavor, shelf life and storability of the final product.







